참조한 강의 : Spring & Hibernate For Beginners (www.udemy.com/course/spring-hibernate-tutorial/)
- Spring MVC Form Tag
HTML 에서 Form 태그를 쓰는 이유는, 간단히 말하면 사용자의 입력을 받아서 서버와 통신을 하기 위함이다.
Spring 의 뷰 템플릿인 JSP 를 쓸때, 일반적인 HTML 처럼 Form 태그를 그냥 써도 되지만,
Spring MVC Form Tag 를 쓰면, Spring Container 가 관리하는, Bean 과 JSP 파일간의 데이터 바인딩 작업을 더 용이하게 해주는 장점이 있다. 더 유용한 이유는, 스프링이 JSP 와 Bean 간의 데이터 전달시에, getter/setter 메소드를 이용해서 전달하기 때문이다.
(만약 이런거 없이 HTML 의 Form tag 로만 받아오려면 HttpServletRequest, @RequestParam 등을 써서 가져와야함. 그러면 코드가 더 길어짐)
몇가지 예제를 통해서, Spring MVC Form Tag 를 어떻게 사용하는지 알아보자
예제 1 - Text Field
먼저 학생에 대한 입력정보를 받아오는 프로그램을 만든다고 가정하고, 다음의 두개의 파일을 만들어보자
첫번째 예제에서는 학생의 이름만 받아오는 부분을 작성해보자.
- Student.java
|
public class Student {
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
public Student() {}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
}
|
cs |
- StudentController.java
|
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/student")
public class StudentController {
@RequestMapping("/showForm")
public String showForm(Model theModel) {
Student theStudent = new Student();
theModel.addAttribute("student", theStudent);
return "student-form";
}
@RequestMapping("/processForm")
public String processForm(@ModelAttribute("student") Student theStudent) {
System.out.println("firstName : " + theStudent.getFirstName() + ", lastName : " + theStudent.getLastName());
return "student-confirmation";
}
}
|
cs |
학생의 정보를 담을 Student 클래스를 만들었고, 이를 URL 매핑시켜서 로직을 처리할 컨트롤러인 StudentController 를 만들었다.
학생정보에 대한 URL 은 /student 를 부모 URL 로 잡으며,
하위 URL 에는
/student/showForm : 학생이 정보를 입력할 수 있는 폼 태그를 보여주는 화면
/student/processForm : 입력 받은 내용을 화면상에 보여주는 화면 으로 지정했다.
이전에는 사용되지 않았던 새로운 어노테이션인 @ModelAttribute 를 사용했다.
이는 모델의 키값을 기반으로 해당 모델의 인스턴스를 리턴하는 어노테이션이다.
컨트롤러와 모델을 정의했으니, 이번엔 뷰를 정의해보자
- student-form.jsp
|
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Student Registration Form</title>
</head>
<body>
<form:form action="processForm" modelAttribute="student">
First name : <form:input path="firstName" />
<br><br>
Last name : <form:input path="lastName" />
<br><br>
<input type="submit" value="submit" />
</form:form>
</body>
</html>
|
cs |
- student-confirmation.jsp
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Student Information</title>
</head>
<body>
The Student name is : ${student.firstName} , ${student.lastName}
<br><br>
</body>
</html>
|
cs |
위 두개의 JSP 파일에서 중요한것은
1. JSTL 을 사용하는 부분에는 JSP 파일 최상단에 아래의 구문을 꼭 써줘야 한다는것
|
1
|
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
|
cs |
2. 기존 HTML 태그와는 다르게 <form:form> , <form:input> 이런식으로 다른 태그를 사용한다는 것
3. <form:form> 태그의 modelAttribute 값은 컨트롤러에서 다루는 모델의 키값이랑 동일한 값을 갖는다는것
(여기선 키값이 student 임)
4. <form:input> 태그의 path 값과 멤버변수 이름이 동일해야 한다는것.
(Student.java 에서 private String firstName, private String lastName 과 JSP 파일의 path="firstName", path="lastName" 두개가 동일한 값을 가져야만 스프링이 찾을 수 있음)
-> 왜 동일한 값을 가져야하는가 하면, 스프링이 이 값들에 대해서 getter/setter 메소드로만, 값 가져오기 및 지정하기를 하기 때문임
이를 실행해보면 다음과 같이 정상적으로 나오게 된다.


예제 2 - Drop Down List
이번에는, Drop Down List 를 만들어보자
여러개의 국가 목록 중에서 자신의 국가를 선택하도록 하는 Drop Down List 를 만들자
먼저 Student.java 에 멤버 변수로 국가정보를 담을 변수를 하나 생성하고 getter/setter 를 추가하면된다.
- Student.java
|
public class Student {
private String country;
public Student() {}
public String getCountry() {
return country;
}
public void setCountry(String country) {
this.country = country;
}
}
|
cs |
그리고 JSP 파일을 수정해야한다
- student-form.jsp
|
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Student Registration Form</title>
</head>
<body>
<form:form action="processForm" modelAttribute="student">
First name : <form:input path="firstName" />
<br><br>
Last name : <form:input path="lastName" />
<br><br>
Country :
<form:select path="country">
<form:option value="BR" label="Brazil" />
<form:option value="IN" label="India" />
<form:option value="KR" label="Korea" />
<form:option value="FR" label="France" />
<form:option value="CO" label="Colombia" />
<form:option value="USA" label="United States Of America" />
</form:select>
<br><br>
</form:form>
</body>
</html>
|
cs |
- student-confirmation.jsp
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Student Information</title>
</head>
<body>
The Student name is : ${student.firstName} , ${student.lastName}
<br><br>
Country : ${student.country}
</body>
</html>
|
cs |
이를 실행해보면, 다음과 같이 나오게 된다.
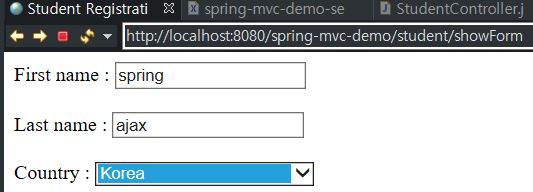
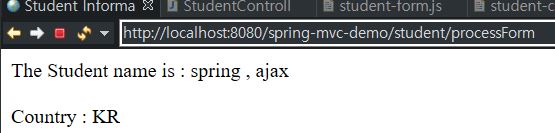
결과가 잘 나오긴 했지만, 위의 student-form.jsp 처럼 국가 각각을 일일이 하드 코딩하는 것은 보기에도 별로 좋지 못하다.
이런 방식 대신에 properties 파일을 불러오게해서, 처리하면 코드양이 더 줄어들것이다.
이를 위해선 properties 파일을 만들고 (주의 : 파일의 위치가 반드시 xml 에서 설정한 값과 일치해야함)
xml 파일에 가서 설정값을 바꿔주고, 자바 코드와 JSP 코드를 다르게 작성해야 한다.
- countries.properties
|
BR=Brazil
FR=France
CO=Colombia
IN=India
KR=Korea
US=United States Of America
|
cs |
- spring-mvc-demo-servlet.xml
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd">
<!-- Add support for component scanning -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.luv2code.springdemo" />
<!-- Add support for conversion, formatting and validation support -->
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
<!-- Define Spring MVC view resolver -->
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/view/" />
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</bean>
<!-- mvc resources mapping -->
<mvc:resources mapping="/resources/**" location="/resources/"/>
<!-- load properties file -->
<util:properties id="countryOptions" location="classpath:../countries.properties" />
</beans>
|
cs |
- StudentController.java
|
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/student")
public class StudentController {
@Value("#{countryOptions}")
private Map<String, String> countryOptions;
@RequestMapping("/showForm")
public String showForm(Model theModel) {
Student theStudent = new Student();
theModel.addAttribute("student", theStudent);
theModel.addAttribute("theCountryOptions", countryOptions);
return "student-form";
}
@RequestMapping("/processForm")
public String processForm(@ModelAttribute("student") Student theStudent) {
System.out.println("firstName : " + theStudent.getFirstName() + ", lastName : " + theStudent.getLastName());
return "student-confirmation";
}
}
|
cs |
Map 을 이용해서 국가 ISO 값을 키값으로, 국가의 이름을 value 로 하는 것으로 정의해주고,
모델에 이 Map 을 추가해준다.
- student-form.jsp
|
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Student Registration Form</title>
</head>
<body>
<form:form action="processForm" modelAttribute="student">
First name : <form:input path="firstName" />
<br><br>
Last name : <form:input path="lastName" />
<br><br>
Country :
<form:select path="country">
<form:options items="${theCountryOptions}" />
</form:select>
<br><br>
</form:form>
</body>
</html>
|
cs |
JSP 코드의 <form:option> 부분이 다 사라지고 <form:options> 한줄로 처리된것을 볼 수 있다.
이것도 실행해보면 동일한 결과가 나온다.
예제 3 - Radio Button
Radio Button 은 <form:radiobutton path="~" value="~" /> 이런형식으로 작성된다.
이번엔 해당 학생이 가장 선호하는 프로그래밍 언어를 선택한다고 해보자
그럴려면, 학생 클래스에 이 값을 담는 멤버 변수가 있어야 하고 getter/setter 가 있어야 한다.
그 후에, JSP 코드 또한 바꿔준다.
- Student.java
|
public class Student {
private String favoriteLanguage;
public Student() {}
public String getFavoriteLanguage() {
return favoriteLanguage;
}
public void setFavoriteLanguage(String favoriteLanguage) {
this.favoriteLanguage = favoriteLanguage;
}
}
|
cs |
- student-form.jsp
|
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Student Registration Form</title>
</head>
<body>
<form:form action="processForm" modelAttribute="student">
Choose your favorite programming languages : <br>
Java <form:radiobutton path="favoriteLanguage" value="JAVA"/>
C++ <form:radiobutton path="favoriteLanguage" value="C++"/>
C# <form:radiobutton path="favoriteLanguage" value="C#"/>
Python <form:radiobutton path="favoriteLanguage" value="Python"/>
<br><br>
</form:form>
</body>
</html>
|
cs |
- student-confirmation.jsp
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Student Information</title>
</head>
<body>
The Student's favorite language is : ${student.favoriteLanguage}
<br><br>
</body>
</html>
|
cs |
실행 결과


(이 예제도 선택 항목을 지정할때, <form:radiobutton /> 태그를 여러번쓰는데, 이를 기피하려면, Student.java 클래스에 이들을 담기 위한 별도의 자료구조를 만들어서 getter/setter 처리를 하던가 아니면, properties 파일을 만들어서 처리하면 된다)
예제 4 - Check Box
체크 박스는 <form:checkbox path="~" value="~" /> 이런식으로 태그를 작성하고, 이번에는 학생이 사용하는 운영체제를 고르도록 해보자.
(주의할것은 Check Box 는 동시에 여러개를 선택할 수 있다. 그래서, JSP 화면에 이들을 보여주기 위해서는, 반복문을 사용해서 보여줘야 하는데, 먼저 JSTL 을 불러올 수 있게 설정해줘야하고, <c:forEach> 라는 새로운 태그를 작성해야한다)
- Student.java
|
public class Student {
private String[] operatingSystems;
public Student() {}
public String[] getOperatingSystems() {
return operatingSystems;
}
public void setOperatingSystems(String[] operatingSystems) {
this.operatingSystems = operatingSystems;
}
}
|
cs |
- student-form.jsp
|
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Student Registration Form</title>
</head>
<body>
<form:form action="processForm" modelAttribute="student">
Choose your operating system : <br>
Ubuntu <form:checkbox path="operatingSystems" value="Ubuntu" />
CentOS <form:checkbox path="operatingSystems" value="CentOS" />
Windows <form:checkbox path="operatingSystems" value="Windows" />
Mac OS <form:checkbox path="operatingSystems" value="Mac OS" />
<input type="submit" value="submit" />
</form:form>
</body>
</html>
|
cs |
- student-confirmation.jsp
|
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Student Information</title>
</head>
<body>
The Student's operating system is
<ul>
<c:forEach var="element" items="${student.operatingSystems}">
<li>${element}</li>
</c:forEach>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
|
cs |
student-confirmation.jsp 에서 <%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %> 를 써서 JSTL 을 불러온다는 점,
그리고 반복된 요소를 출력하기 위해서 <c:forEach var="element" items="${student.operatingSystmes}"> 를 사용한다는점에 주목해서 사용하면된다.
실행 결과


여기까지 Spring MVC Form Tag 에 대해서 간단한 사용법을 알아봤다.
다음은 Form 으로 부터 입력 받은 값들에 대해서 유효성 검증을 하는 방법을 알아본다.
'Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Spring Framework - Hibernate ORM (0) | 2021.02.02 |
|---|---|
| Spring Framework - Validation (0) | 2021.02.01 |
| Spring Framework - MVC 코드 예제 (0) | 2021.01.27 |
| Spring Framework - Spring MVC Overview (0) | 2021.01.27 |
| Spring Framework - XML 파일 없이 스프링 설정하기 (0) | 2021.01.22 |